7 Jabotinsky st. Moshe Aviv tower, 19th floor. Ramat-Gan
7 Jabotinsky st. Moshe Aviv tower, 19th floor. Ramat-Gan
Congenital moles or congenital nevi are pigmented skin lesions that are either present at birth or appear shortly thereafter.
These moles are characterized by an increased number of melanocytes, the pigment-producing cells in the skin. They can vary in size, shape, and color, ranging from small and flat to large and raised.
One important aspect of congenital moles is their potential for growth and changes over time. They may undergo transformations such as darkening, thickening, or the development of additional pigmentation. While the majority of congenital moles are benign and pose no health risks, large or giant moles carry an elevated risk of developing melanoma, a type of skin cancer. The risk of malignant transformation is particularly heightened for larger congenital moles, especially those exceeding 20 centimeters in diameter at maturity.
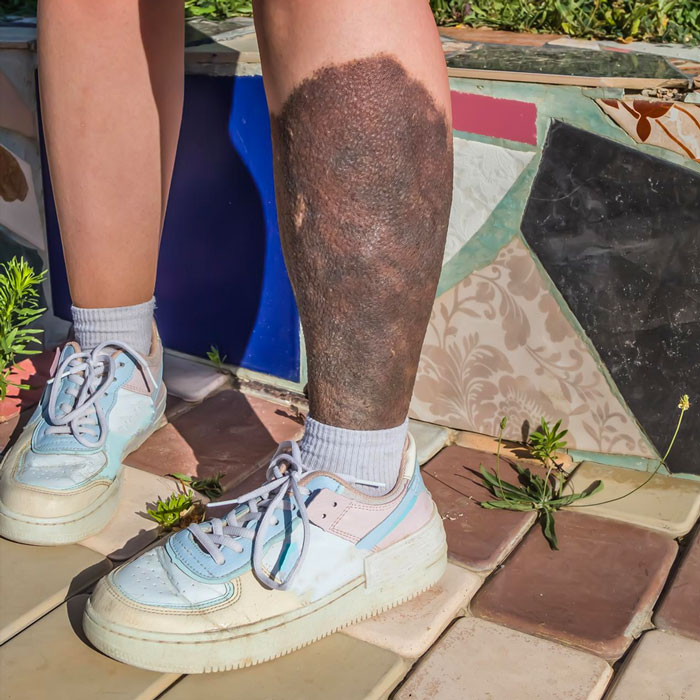

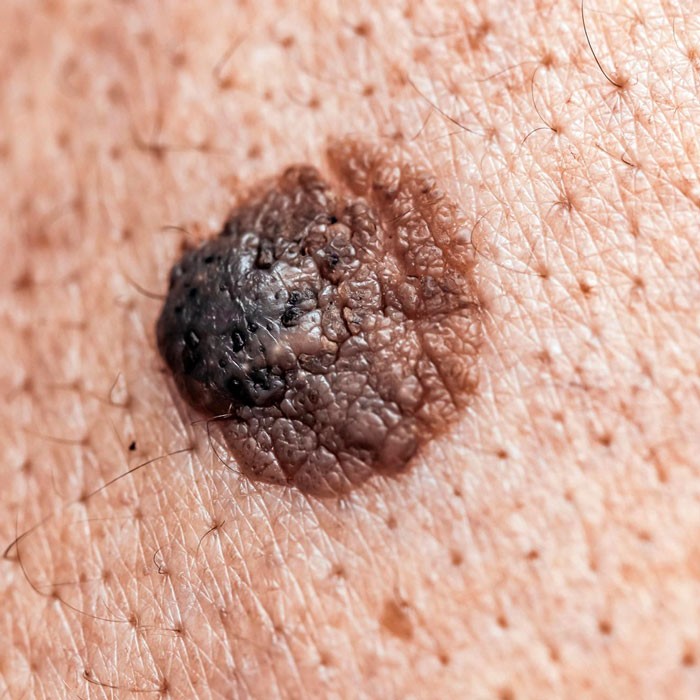
The management and treatment of congenital moles depend on factors such as size, location, and associated risk factors. Small and medium-sized moles located in non-sensitive areas usually do not require immediate intervention. However, regular follow-up with a dermatologist is recommended to promptly address any changes or signs of malignancy.
Larger moles or those situated in high-risk areas, such as the scalp or genital region, may require a more proactive approach. Dermatologists may conduct periodic evaluations to monitor mole changes and may recommend a biopsy if suspicious features or concerning signs emerge. In certain cases, surgical removal or reduction techniques may be considered to mitigate complications or enhance cosmetic appearance. The decision to undergo surgical intervention is typically based on a thorough assessment of the mole’s characteristics and the individual’s overall health.
It is important to note that most congenital moles do not necessitate treatment beyond monitoring. However, individuals with congenital moles should take precautions to protect their skin. This includes employing sun protection measures such as wearing protective clothing, regularly applying sunscreen, and seeking shade during sunny hours. Minimizing sun exposure is crucial, as excessive UV radiation may heighten the risk of melanoma development in a birthmark.
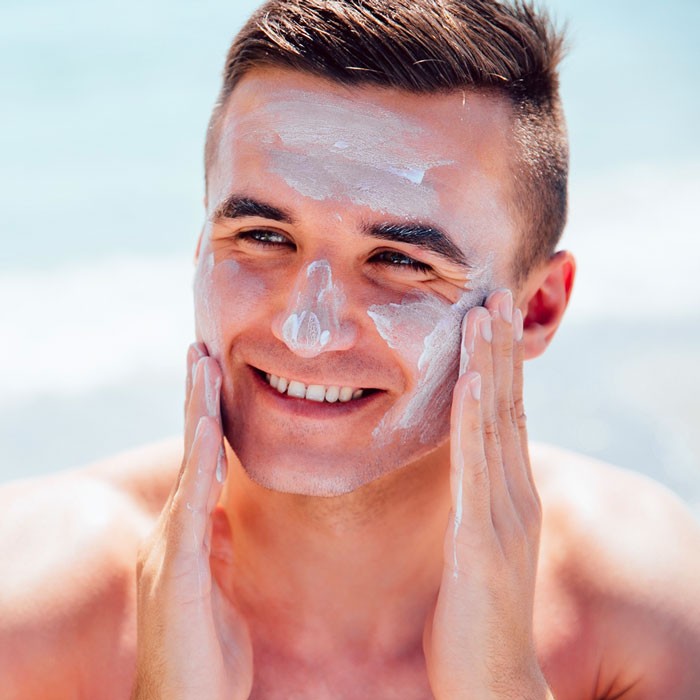

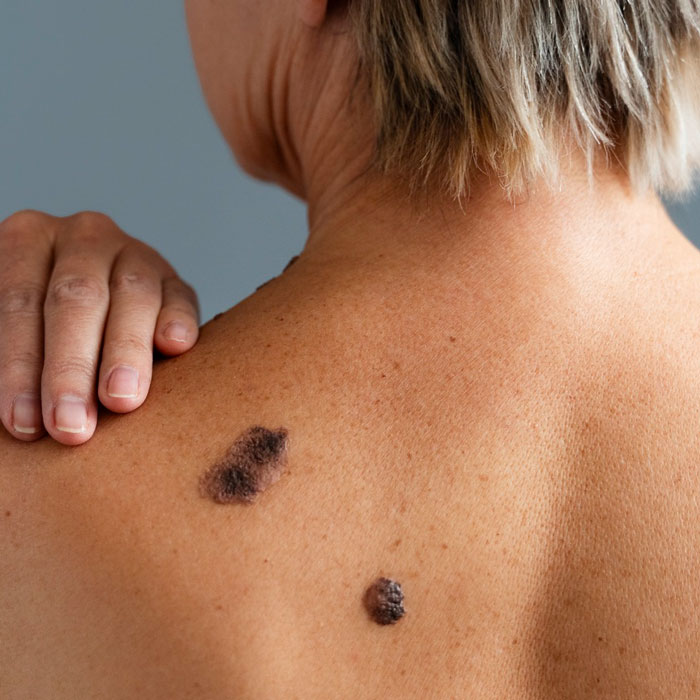
In addition to physical consequences, individuals with large or giant congenital moles may encounter emotional and psychological challenges. The visible presence of these moles can impact self-esteem and body image, especially during adolescence.
Congenital moles are pigmented skin lesions that are present at birth or emerge shortly thereafter. While the majority are benign, large or giant moles may have an increased risk of developing into melanoma. Regular follow-up with a dermatologist specializing in skin cancer is essential to detect any changes or signs of malignancy early on. Sun protection measures should be adopted, and parents of children with large or giant congenital moles should be mindful of potential emotional and psychological effects. With appropriate management, support, and precautions, the vast majority of individuals with congenital moles can lead lives free from negative consequences or complications.
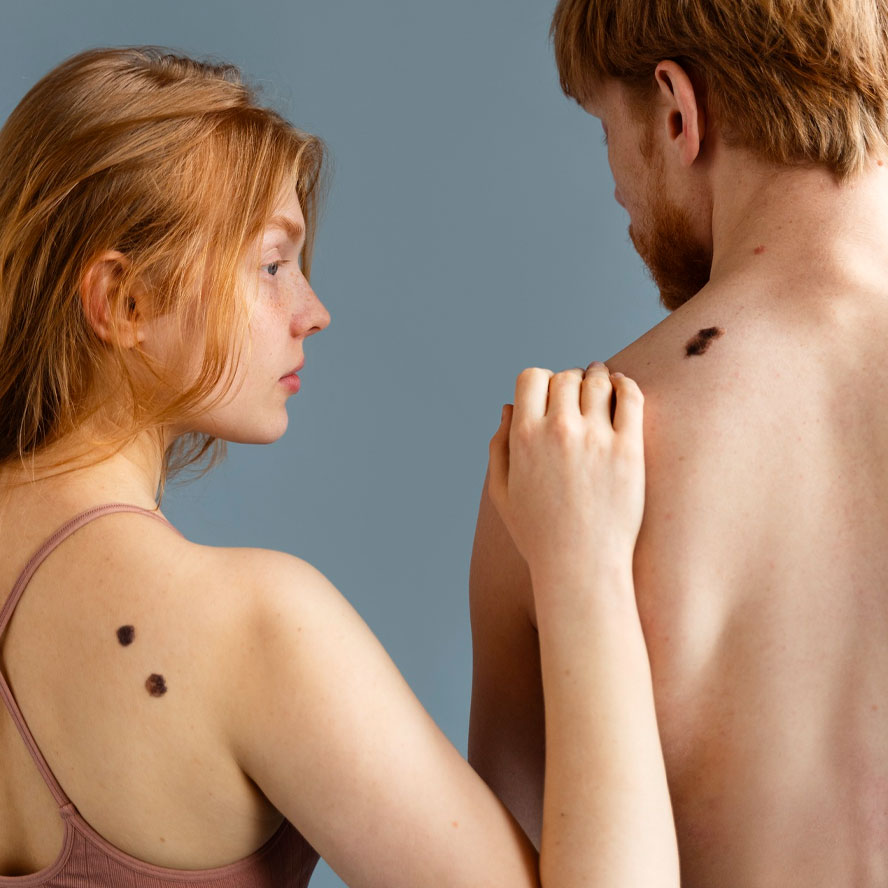

If you have located a suspicious lesion on the skin, especially if it is unusual, new or recently changed, contact a dermatologist as soon as possible in order to diagnose the lesion and decide on further treatment.
Give us a call or fill in your details and we will get back to you