7 Jabotinsky st. Moshe Aviv tower, 19th floor. Ramat-Gan
7 Jabotinsky st. Moshe Aviv tower, 19th floor. Ramat-Gan
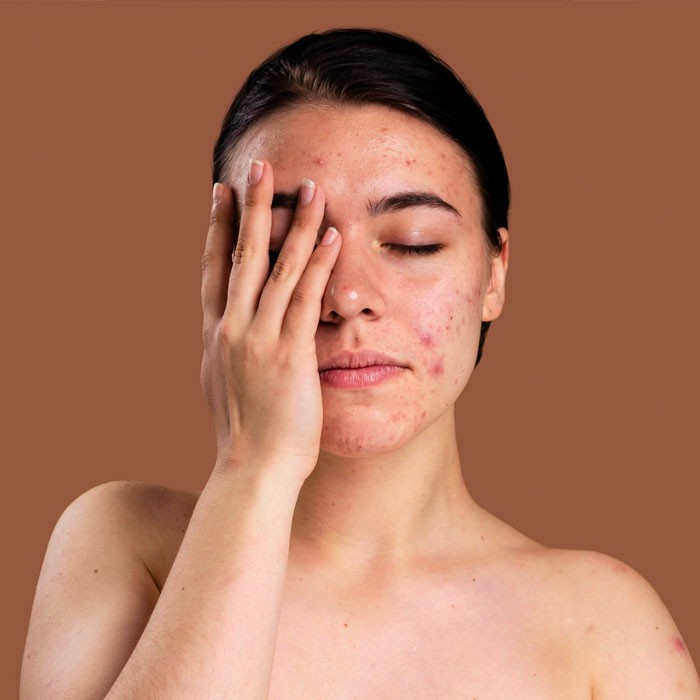
The management and treatment of acne involve a multifaceted approach aimed at reducing the severity of existing acne lesions, preventing new breakouts, and minimizing the risk of scarring.
The treatment options for acne can vary depending on the type and severity of acne, as well as individual factors such as skin type and medical history.
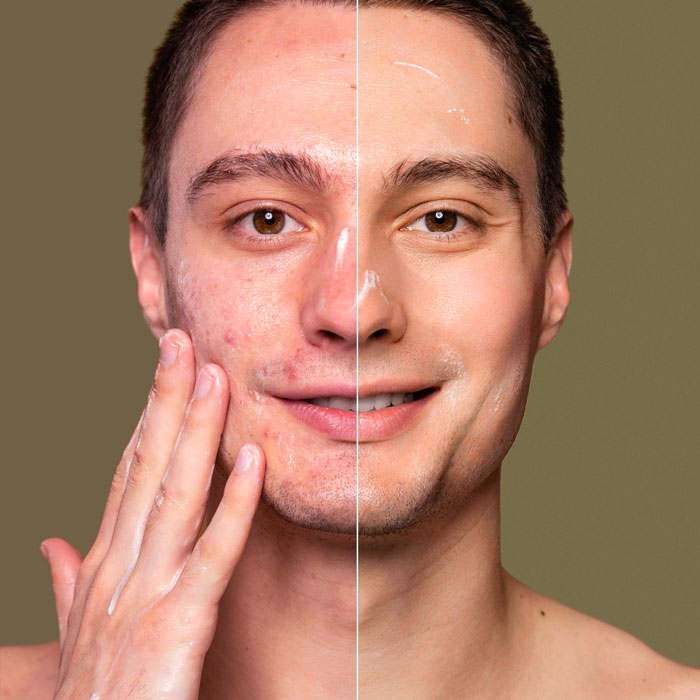


Topical treatments are commonly used as a first-line approach for mild to moderate acne. These include products containing ingredients like benzoyl peroxide or salicylic acid, which help unclog pores, reduce inflammation, and promote skin cell turnover. Additional topical medications, such as topical antibiotics or retinoids, may be recommended for more severe cases.
Oral medications, such as antibiotics, hormonal therapies (such as oral contraceptives or spironolactone), or isotretinoin (commonly known as Accutane), may be prescribed for moderate to severe acne that does not respond to topical treatments. These medications target the underlying causes of acne, such as bacteria, hormonal imbalances, or excessive sebum production.
In addition to medications, other treatment modalities may be employed to manage acne. These include procedures like chemical peels, microdermabrasion, or light-based therapies, which help exfoliate the skin, reduce inflammation, and kill acne-causing bacteria. In some cases, extraction of comedones or cysts by a dermatologist may be necessary.
It is important to note that a consistent skincare routine, including gentle cleansing, avoiding excessive scrubbing or picking at acne lesions, and using non-comedogenic products, can significantly contribute to the management of acne. Regular follow-ups with a dermatologist are essential to monitor progress, adjust treatment plans if needed, and address any concerns or side effects.
Overall, the management and treatment of acne require a comprehensive and personalized approach to effectively control breakouts, improve the appearance of the skin, and prevent long-term complications such as scarring. With the guidance of a dermatologist and adherence to a tailored treatment regimen, individuals can achieve clearer, healthier skin.
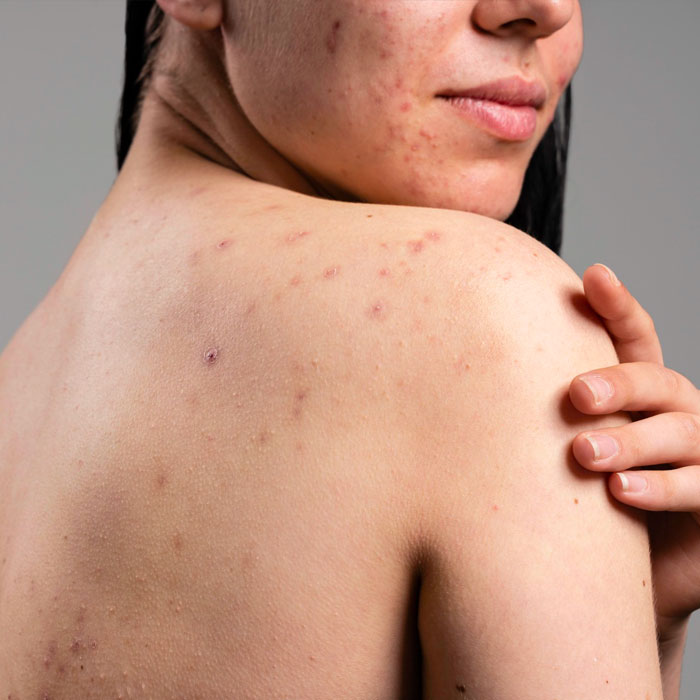
If you have located a suspicious lesion on the skin, especially if it is unusual, new or recently changed, contact a dermatologist as soon as possible in order to diagnose the lesion and decide on further treatment.
Give us a call or fill in your details and we will get back to you